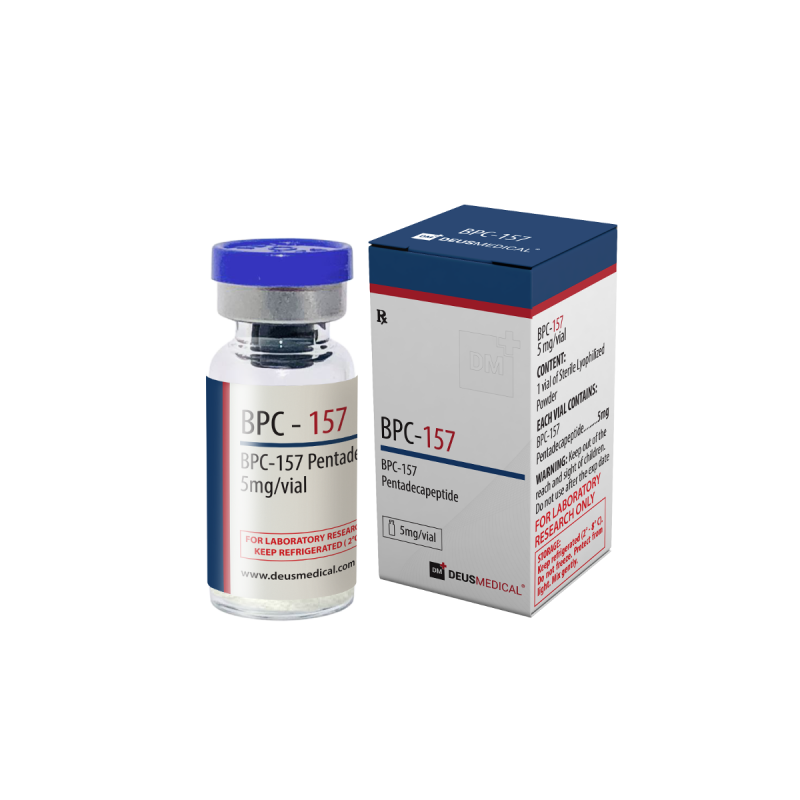
BPC-157 - Deus Medical - US
CLASSIFICATION Polypeptides
ACNE No
WATER RETENTION No
HBR No
HEPATOTOXICITY No
AROMATIZATION No
MANUFACTURER Deus Medical - US
WAREHOUSE USA Warehouse 6
SUBSTANCE
BPC-157 Pentadecapeptide,

BPC-157
By increasing the number of new blood vessels, this could help with IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Diseases), in which the healing of the intestinal lining is slowed down by inflammatory processes. In addition, BPC-157 may promote wound and tendon healing by blocking the growth-inhibitory effects of a specific molecule called 4‐hydroxynonenal.
It may also help tendons heal by causing tendon cells to produce more receptors for certain growth factors. This, in turn, allows the cells of the tendon to grow during the repair of the injury, thus speeding up the process. It can also reduce inflammation, a process which is likely involved in its effects on wounds, ulcers, and tissue protection.
BPC-157 can also influence the activity of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which may help treat depressive disorders and chronic pain.
It can increase the production of nitric oxide (NO), which lowers blood pressure.
Lastly BPC-157 also appears to allow fibroblasts, which are a specific type of connective tissue cell found in skin, tendons, and other hard tissues in the body, to grow and spread faster, which may be useful in injuries related to joints.
HOW TO USE:
It can be administered either orally or by injection (although based on user experience, injectable is often preferred for muscle injuries and oral for stomach health) and the human equivalent dose is approximately 1.6mcg/kg body weight per day, although a dose of 5.4mcg/kg per day is usually recommended, for a period of at least 2 weeks.